Technical Measurement Units link numbers/data with physical quantities. They are important in helping us understand the property of something. These three types of measurements help us determine if the technology will be a good fit for our needs and can help to determine our limitations. New technologies are consistently pushing the limits of what we know today as the technical measurement limitation. Technical Measurements are important for IT Professional when determining the requirements of systems and hardware. Incorrect measurements can cause poor performance is product quality. Here are three important measurements to know and understand when determining the scope of device.
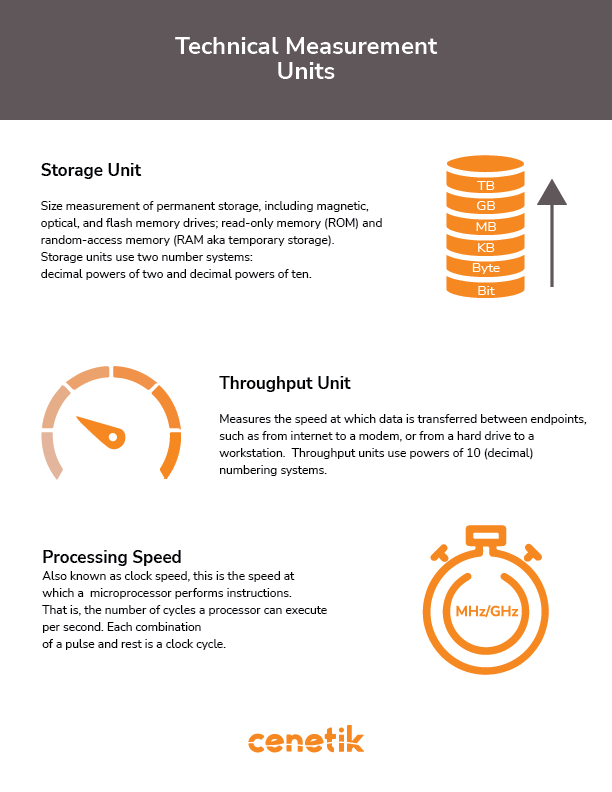
Storage Units
The two most commonly used data storage capacity is bit and byte. Bits only have two states (0,1), and Bytes which has eight bits. Larger units of measure, utilize Multiples of byte. Here are a few types of storage units:
- Kilobyte (KB) – is the next largest unit of measurement than a byte. The kilobyte is 1,000 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 10 and 1,024 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 2.
- Megabyte (MB) – is equal to 1,000 kilobytes. The megabyte is 1,048,576 bytes. The megabyte is 1,000,000 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 10 and 1,048,576 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 2.
- Gigabyte (GB) – is equal to 1,000 megabytes. The gigabyte is 1,000,000,000 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 10 and 1,073,741,824 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 2.
- Terabyte (TB) – is equal to 1,000 gigabytes. The terabyte is 1,000,000,000,000,000 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 10 and 1,125,899,906,842,620 bytes when expressed in decimal powers of 2.
Throughput Unit
Throughput is measure by the speed at which data is transferred between two terminations. One example is from a hard drive to a computer. Here are a few examples of speeds and technology that utilized that throughput:
- Bits per Second (bps) – measure the speed of early dial-up/analog internet modems.
- Kilobit per Second (Kbps) – measure the speeds of early DSL internet connections.
- Megabit per Second (Mbps) – measure the speeds of broadband internet connections and I/O devices (USB 1.1, USB 2.0).
- Gigabit per Second (Gbps) – measure the speeds of high-speed internet connections high-performance device (USB 3.1 Gen, USB 3.1 Gen 2)
- Terabyte per Second (Tbps) – measure the speeds of internet connections between countries and provinces.
Processing Speed
AKA clock speed, is the speed at which a microprocessor completes instructions. A clock cycle is a combination of pulse and rest. Here are the two types of processing speeds:
- Megahertz (MHz) – is equal to 1,000,000 cycles per second
- Gigahertz (GHz) – is equal to 1,000,000,000 cycles per second
