Data transfer is limited by both speed and distance. The faster the data is transferred, the shorter the distance it can travel. This means that if you want to transfer data over a long distance, you need to use a higher speed connection. On the other hand, if you need to transfer data over a short distance, then you can get away with using a lower speed connection.
The amount of data that can be transferred in one go is also limited by the speed and distance of the connection being used. Therefore, if you want to transfer large amounts of data quickly and efficiently, then it’s important that your connection has sufficient bandwidth and is capable of transferring data at high speeds over long distances.
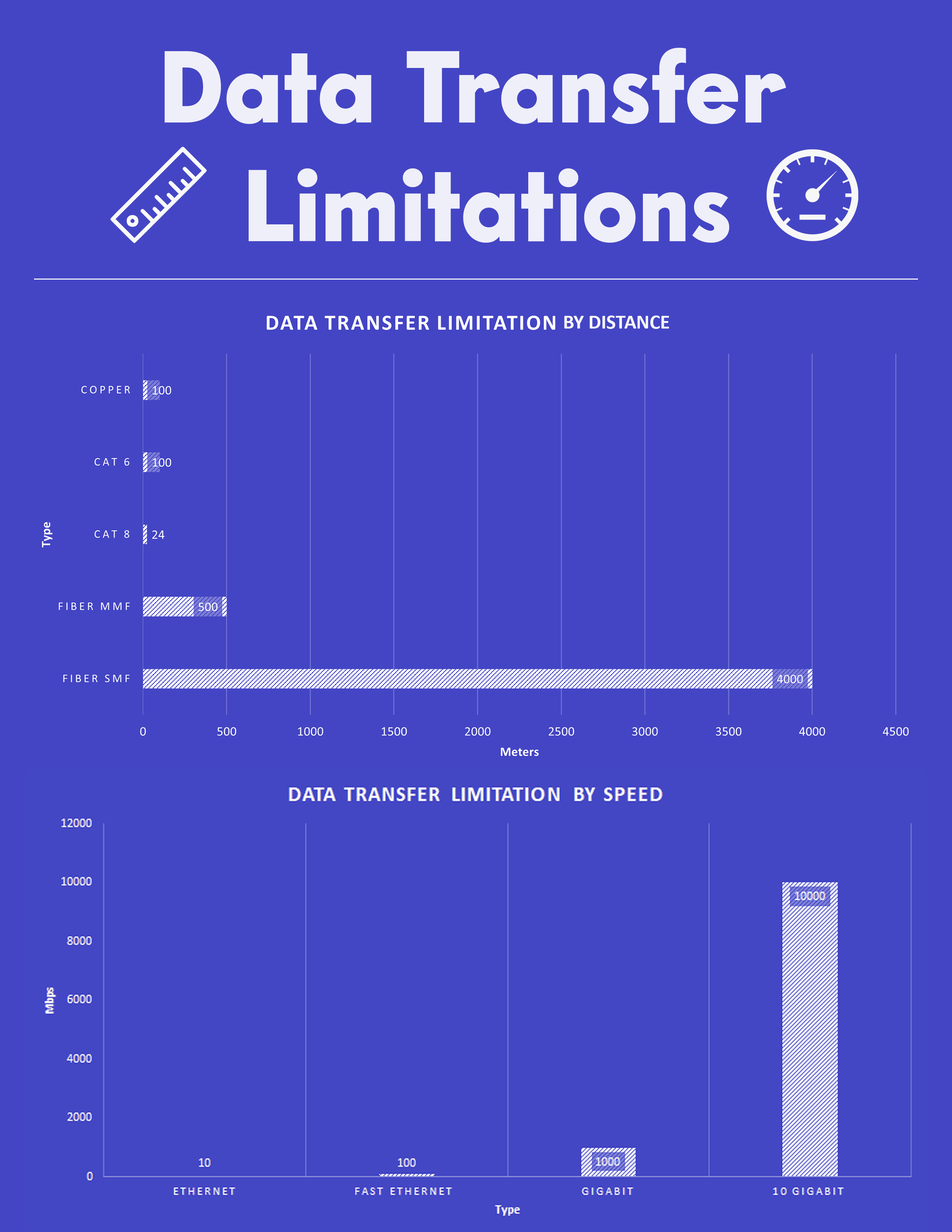
In this article, we examine different physical cabling data transfer limitation. Copper wire, Fiber Optic cable, and Ethernet cables are the three basic categories of data cables. It can be challenging to comprehend which kind of cable should be used for your project if you are not an IT expert. The length of the cable, the data transmission rates needed, and the environment in which the cable will be used are just a few of the many considerations when choosing the right kind of cable. Here is the breakdown by cable type:
Copper
Since copper is a great conductor of heat and electricity, copper cables have been used in wiring ever since analog landlines were first introduced, if not before. Despite being limited to one or a few buildings, tiny networks may nevertheless benefit from copper cabling.
Maximum Distance Limitation: 100 Meters
CAT 6
One of the most widely used internet technology standards is Ethernet. A LAN network wouldn’t be complete without an Ethernet wire. This cable connects the various components of a network. The sixth generation of Ethernet cabling, known as CAT6, is used in residential and commercial networks. It is also the “typical” cabling standard in contemporary office buildings. The CAT5e and CAT5 standards that came before it are backwards compatible with CAT6.
Maximum Distance Limitation: 100 Meters
CAT 8
One of the most widely used internet technology standards is Ethernet. A LAN network wouldn’t be complete without an Ethernet wire. This cable connects the various components of a network. The official replacement for Cat6A cabling is Category 8. Cat8 cabling’s main advantage is faster throughput over close distances. Due to these distance restrictions, a data center would be the ideal location for Cat8 to be used for connecting network equipment.
Maximum Distance Limitation: 24 Meters
Multi-mode Fiber (MMF)
Multiple light modes can be supported simultaneously by multi-mode fiber. Multiple light modes with lower brightness and higher attenuation must be sent over multimode fiber. As a result, there are five different grades of multimode fiber, each with a different amount of bandwidth and range. The maximum transmission distance for multi-mode fiber is significantly reduced.
Maximum Distance Limitation: 500 Meters
Single-mode Fiber (SMF)
A single light mode is intended to be propagated by single-mode fiber. Brighter, more powerful light sources are supported by single-mode fiber cables with less attenuation. Additionally, one light mode offers theoretically limitless bandwidth. No matter the signal’s bandwidth or resolution, single-mode fiber can enable both short- and long-distance transmission. Due to brighter light sources and more complex optical processors, single mode electronics typically cost more.
Maximum Distance Limitation: 4,000 Meters
